Ingesting data from RDBMS into a Snowflake Data Lake using Snowpark
The Calibo Accelerate platform supports ingesting data into a Snowflake data lake using Snowpark. Data is processed within Snowflake avoiding any data movement. This simplifies the architecture and effectively improves the performance of the ingestion pipeline.
Currently the Calibo Accelerate platform supports the following RDBMS data sources for data ingestion into Snowflake data lake using Snowpark:
-
MySQL
-
PostgreSQL
-
Oracle
To create a data integration job using Snowpark
-
Sign in to the Calibo Accelerate platform and navigate to Products.
-
Select a product and feature. Click the Develop stage of the feature and navigate to Data Pipeline Studio.
-
Create a data pipeline with the following stages:
Data source (MySQL) > Data Integration (Snowpark) > Data Lake (Snowflake)
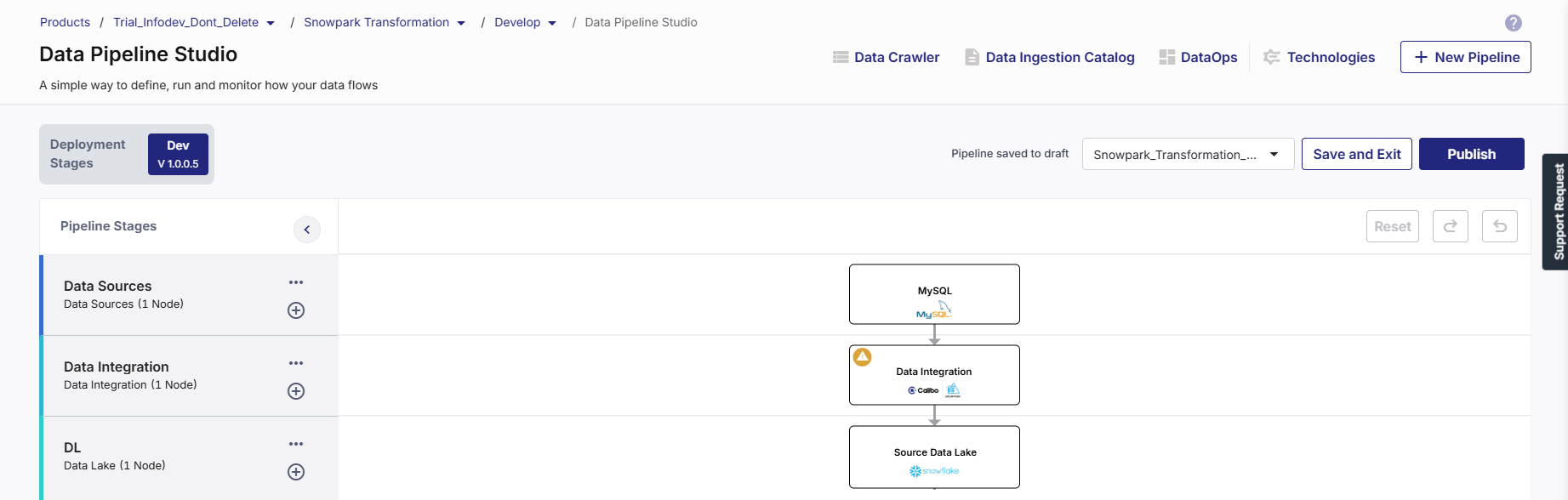
-
Add MySQL in the data source stage and Snowflake in the data lake stage and configure both the nodes. To know more about configuring the source node, see Data Sources.
-
In the data integration node, add Snowpark and do the following:
-
Provide a technology title.
-
Select a Snowpark instance.

Note:
The Snowpark integration node must be configured using the same Snowflake account that is used in the data lake stage.
-
Click Save.
-
-
Click the Snowpark node and click Create Job.

-
Complete the following steps to create the Snowpark integration job:
 Job Name
Job Name
Provide job details for the data analyzer job:
-
Template - Based on the source and destination that you choose in the data pipeline, the template is automatically selected.
-
Job Name - Provide a name for the data integration job.
-
Node Rerun Attempts - Specify the number of times the pipeline rerun is attempted on this node of the pipeline, in case of failure. The default setting is done at the pipeline level. You can change the rerun attempts by selecting 1, 2, or 3.
-
Fault tolerance - Select the behavior of the pipeline upon failure of a node. The options are:
-
Default - Subsequent nodes should be placed in a pending state, and the overall pipeline should show a failed status.
-
Skip on Failure - The descendant nodes should stop and skip execution.
-
Proceed on Failure - The descendant nodes should continue their normal operation on failure.
-
Click Next.
 Source
Source
In this stage, the source details are auto-populated depending on the options that you have configured for the source node. You can view the following information:
-
Source
-
Datastore
-
Selected table
-
Options selected like Configure Historical or Configure Incremental.
Click Next.
 Target
Target
In this stage, you can select the warehouse, database, schema for the target, map the source data to target tables, and enable object tagging and add tags.
-
Target - This field is auto-populated, based on the configured target node.
-
Datastore - This field is auto-populated, based on the configured datastore in the target node.
-
Warehouse - This field is auto-populated. You can select a different warehouse for the target.
-
Database - This field is auto-populated. You can select a different database for the target.
-
Schema Name - This field is auto-populated. You can select a different schema for the target.
-
Map source data to target tables - Map the source file to a target table.
-
Source - Select a source file from the dropdown.
-
Target Table - Select a target table to map with the selected source file. You can either select an existing table or create a new one.
Click Add Mapped Tables.
-
-
Follow the steps above to map more than 1 table.
Click Next.
 Schema Mapping
Schema Mapping
In this stage, you must provide the schema mapping details for all the mapped tables from the previous step.
-
Mapped Data - Select a mapping.
-
Infer Source Schema - This toggle if turned on, identifies the schema with data types for the columns automatically. If you turn off the toggle you can manually edit the data types.
-
Auto-Evolve Target Schema - This toggle if turned on allows the addition of columns in the target table if a column is added to the source table. If this toggle is turned off and there is schema change in the source table, then the job fails.
-
Filter columns from selected table - In this section, deselect the columns that you want to exclude from the mapping. Select a constraint to run on the source column. Only if the constraint is fulfilled, the column is mapped to the target.
-
SET NOT NULL - this means that the column should not have a null value.
-
CHECK - Select a boolean expression and value for the condition.
-
-
Continue job run even if constraints are not met - This toggle ensures that the job run is continued even if a constraint is not met.
-
Add Custom Columns - Enable this toggle if you want to add custom columns.
-
Column - Provide a column name.
-
Type - Select a type from the following options:
Type Description Static Parameter Provide a static value. The custom column is checked for that value. System Parameter Select a custom column from the dropdown list. The custom column is checked for the value. Generated Parameter Add a SQL expression to concatenate the value from the selected column and add it to the custom value. -
Click Add Custom Column.
-
-
Click Add Schema Mapping.
Click Next.
A summary is displayed on the next screen. You can perform the following operations:
-
View Details
-
Edit
-
Delete
 Data Management
Data Management
In this stage, you select the operations to perform on the data. You must provide data management details for all the mapped tables.
-
Mapped Data - Select the mapped table for which you want to select data operations.
Data Management for Mapped Tables
-
Operation Type - Select a data operation to be performed from the following options:
-
Append
-
Merge
-
Click Next.
 Additional Parameters
Additional Parameters
In this stage you use existing objects or create new objects to provide access to Snowflake services and resources required to run the Snowpark integration job.
Select one of the following options:
-
Create New Objects - Use this option to create new objects. to create a new boject do the following:
-
Check if you have sufficient privileges to create new objects.
-
If Use Credentials from Snowflake Configuration is enabled in the Snowpark Configuration, proceed to create the objects.
-
If Use Credentials from Snowflake Configuration is disabled, provide your credentials and use them to create the new objects.
-
-
Use Existing Objects - To use any of the existing objects, ensure that you have access to the object. Select one or more of the following objects:
-
Secret - These are credentials, API keys, or other data required to access Snowflake services and resources.
-
Network Rule - This controls and restricts access to and from Snowflake environment and resources.
-
Access Integration - This enables secure and controlled access to specific external locations and resources from within the Snowflake environment.
-
Click Next.
 Notifications
Notifications
You can configure the SQS and SNS services to send notifications related to the node in this job. This provides information about various events related to the node without actually connecting to the Calibo Accelerate platform.
SQS and SNS Configurations - Select an SQS or SNS configuration that is integrated with the Calibo Accelerate platform. Events - Enable the events for which you want to enable notifications:
-
Select All
-
Node Execution Failed
-
Node Execution Succeeded
-
Node Execution Running
-
Node Execution Rejected
Event Details - Select the details of the events from the dropdown list, that you want to include in the notifications. Additional Parameters - Provide any additional parameters that are to be added in the SQS and SNS notifications. A sample JSON is provided, you can use this to write logic for processing the events. -
-
| What's next? Snowpark Custom Transformation Job |